Which is better – paper or film
For many years plastic packaging has been very popular. Last few years we are more and more often meeting with the message that plastics are the source of many problems of our times and the future is ecological packaging such as paper. In the following short article I will try to help to present and bring some facts about the advantages and disadvantages of this type of packaging material
What is foil
Film can be made from fossil fuels such as oil, or from bio-based materials such as sugar cane, cellulose, starch, etc. Plastics made from both types of raw materials can be highly durable, non-biodegradable or biodegradable and compostable. The type of raw material used to manufacture a plastic does not necessarily determine how a product will behave at the “end of its life”, e.g. films made from bio-based materials do not mean that they will always biodegrade.
Plastic films are most often manufactured by extrusion blow moulding or pouring, i.e. flat-slot extrusion.
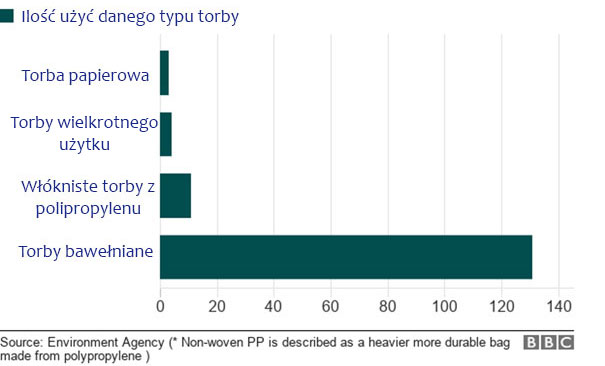
How many times should we use a given type of shopping bag compared to a traditional plastic one, so that the environmental impact is at the same level
Which films are better – oil-based or derived from bio-based materials
Here, unfortunately, there is no one right answer. When examining the carbon footprint over the entire life cycle of a plastic, e.g. film, bioplastics generally have a smaller impact on the carbon footprint during production. Fossil fuel-based plastics emit greenhouse gases during their manufacture (refineries) but are considered inert in landfills. When bioplastics degrade, they can emit large amounts of methane, but can be considered carbon neutral during energy recovery. For all plastics, recycling generates the lowest environmental burden.
What kind of films Polpack company offers
Polpack Company offers heat-shrinkable films such as PVC and polyolefin, hand and machine stretchf ilms, pre-stretched and high-stretched and films for manufacturing cushions for parcel filling.
As a company aware of its responsibility for the environment, we are systematically implementing ecological films into our offer. Since 2020, we have been producing DECOLINE DCL-BD biodegradable thermo-shrinkable polyolefin film, and we are planning to introduce polyolefin films manufactured largely from PCR raw materials. As an ecological alternative to traditional stretch film we offer biodegradable machine stretch films and those made from post-consumer waste materials (PCR). Our offer of ecological packaging solutions is complemented by air bags made of at least 50% PCR raw materials.
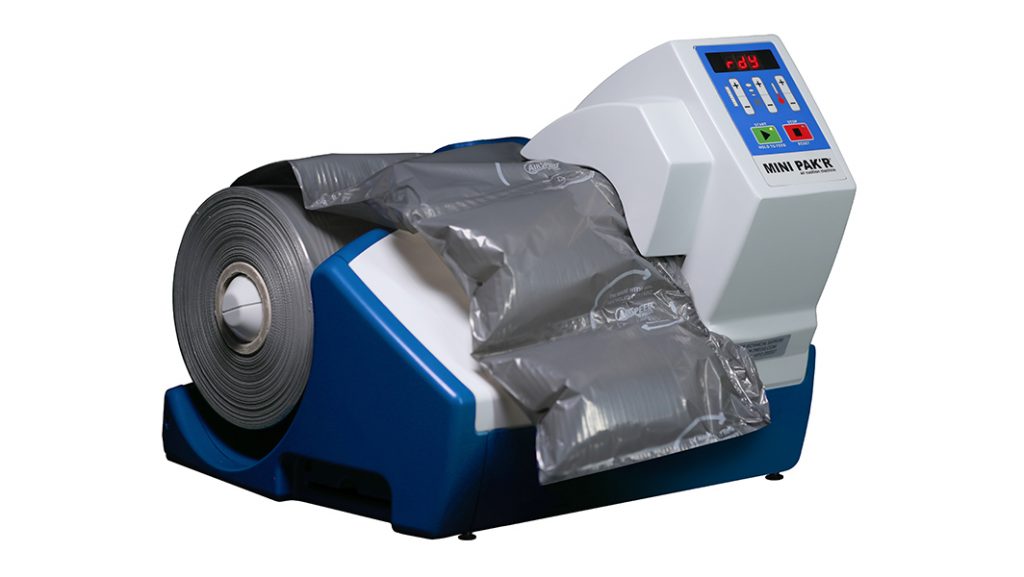

Eco-friendly cushions to fill the empty space in the pack – made from at least 50% PCR raw materials
What kind of paper packaging can be found in our offer
We mainly offer paper filling systems for parcels. Our kraft paper for filling is FSC certified (FSC-C134738). Depending on the need, we use different grammages and widths of paper so that the shipped product is best protected while optimizing costs. Our offer of paper solutions for the e-commerce industry is complemented by paper from the so-called green-line series, i.e. recycled paper.
Can films be recycled
Yes, all films offered by Polpack can be recycled. Polyethylene films, polyolefins, films for making air bags and stretch films should be segregated as LDPE materials (code 4), polypropylene films (mainly used for packing on flow-pack machines) are marked as PP (code 5). PVC heat-shrinkable films after use are placed in PVC containers (code 3)

Recycling symbols for films available in Polpack’s offer
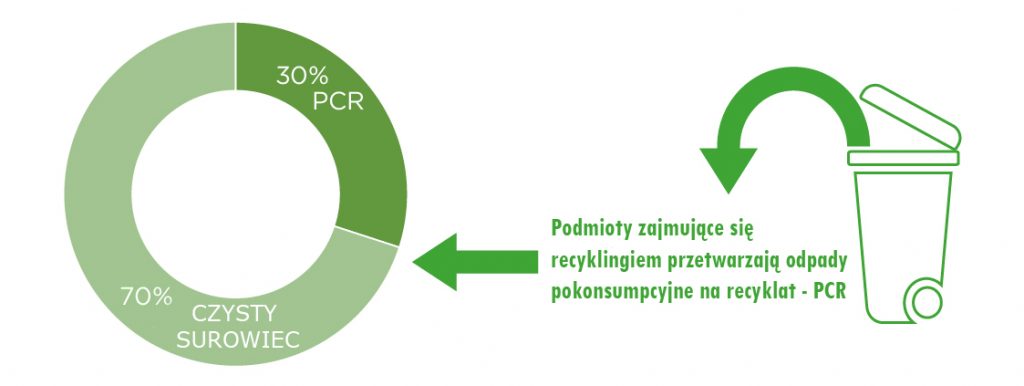
What are films with the addition of PCR plastics
PCR raw materials are a great solution for reducing plastic waste. PCR Post-Consumer Recycled is actually raw materials extracted from post-consumer plastic waste. Depending on the future use of the film, we can use from 20% of PCR raw materials (e.g. for the production of highly transparent heat-shrinkable films) to as much as 90% (e.g. pads for filling parcels).
Landfill plastic takes hundreds of years to decompose and manufacturers use new granulates to make plastic packaging, leaving an ever-increasing carbon footprint. So by using PCR raw materials, we give packaging a new lease of life and reduce the carbon footprint.
What are biodegradable films?
An example of biodegradable film is DECOLINE DCL-BD. The biodegradable film we produce consists of 20% renewable raw material from sugarcane ethanol, which significantly reduces the film’s carbon footprint. DCL-BD shrink film contains additives which, when accidentally discarded into the environment, help the film to become environmentally friendly so that bacteria and fungi can decompose it into products such as CO2, H2O and biomass. Importantly, DECOLINE DCL-BD film leaves no micro plastic behind and is 100% recyclable.
Which is better – foil or paper packaging?
It is difficult to give a clear answer to this question. Plastic packaging was originally designed as an environmentally friendly alternative to paper and cotton packaging (e.g. bags). For example, to produce a single-use plastic bag we use ¼ of the energy needed to produce a paper bag. Unlike plastic packaging (which is made from petroleum refinery waste), paper requires forests to be cut down to produce the packaging material. The production process of paper packaging also results in a higher concentration of toxic chemicals compared to the production of, for example, single-use plastic bags.
Plastic packaging is also much lighter and takes up less space than other packaging, so considering transport and storage is also important for ecology. The estimated volume ratio of plastic packaging to paper packaging is 1 to 7. Plastic waste (not only carrier bags) is more compressible than paper – so theoretically it takes up less space in landfills (in % terms) compared to paper packaging.
The biggest problem with plastic packaging is that it is incorrectly segregated or not segregated at all. Due to incompetent waste management we hear more and more often that plastic causes complications and death of marine fauna, and its tiny particles are found in living organisms. That is why it is so important to segregate packaging properly, recycle and reuse it.
The advantage of paper packaging is that it is neutral for the environment, assuming that the consumer throws such packaging away, e.g. to the forest.
Myth: Paper packaging is more sustainable than plastic packaging because it comes from renewable resources.
Fact: life cycle science studies show that plastic packaging is greener at the production stage and more durable (reusable). They also have a smaller carbon footprint!
Plastic tax
On 1 January 2021, the so-called plastic tax came into force throughout the European Union. Member States will pay EUR 0.80 for every kilogram of plastic packaging that is not recycled.
The tax is intended to assist the budget in the fight against the coronavirus pandemic and to promote recycling and a closed-loop economy. The new tax does not as force producers to design packaging that can be easily recycled. Importantly, the tax will not apply to plastic packaging that contains at least 30% recycled material.
Advantages and disadvantages of plastic packaging:
- Low volume and weight
- Durable, long life, which is also their biggest disadvantage
- Good protection against external factors
- Improve the appearance of the packaged product (e.g. shrink films)
- Recyclable
- Cited as one of the main culprits for littering our planet
Advantages and disadvantages of paper packaging:
- Unlike plastic, it biodegrades much faster in the environment
- Good thermal insulation
- Poor barrier properties (they absorb odours, moisture)
- Harmful additives (adhesives, dyes)
- Large amounts of water, CO2 and electricity needed for paper production
- Volume
- Problematic recycling of pseudo paper packaging (paper laminates)
Kamil Woliński
